Flight tracking systems are critical components of modern aviation. These systems provide real-time information on an aircraft’s position, speed, altitude, and other key data during its journey. They help air traffic controllers, airlines, and passengers stay informed and ensure safe and efficient flights. In this article, we explore how flight tracking systems work, the technology behind them, and their role in the aviation industry.
Types of Flight Tracking Systems
Flight tracking relies on several technologies to monitor and record an aircraft’s movement. The most common tracking systems used today include radar-based systems, satellite-based systems, and ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast). Each plays a role in ensuring aircraft are continuously monitored throughout their flight.
Radar-Based Tracking
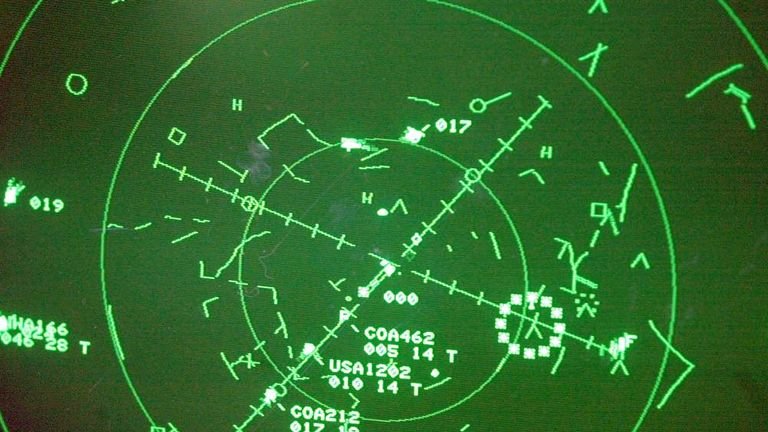
Radar-based tracking is one of the oldest and most widely used methods of monitoring aircraft. Ground-based radar systems send out signals, which bounce off aircraft and return to the radar station. By calculating the time it takes for the signal to return, the system can determine the aircraft’s distance and position.
While radar works effectively in most regions, its coverage is limited to line-of-sight. This means it is less useful over oceans or remote areas, where radar signals cannot reach.
Satellite-Based Tracking
Satellite-based tracking uses global positioning systems (GPS) to track aircraft. This system works by receiving signals from satellites orbiting the Earth, providing global coverage, including areas where radar cannot reach. Satellite-based systems offer continuous monitoring, improving the accuracy of flight data, especially over oceans and remote regions.
One of the most advanced satellite systems in use today is Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B), which transmits real-time data from aircraft to ground stations and other aircraft.
Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B)
ADS-B is a modern, more efficient tracking system that allows aircraft to transmit their GPS position and other important information to air traffic control systems and other nearby aircraft. This system has significantly improved aircraft tracking over large areas and is especially useful for tracking flights in remote or oceanic regions.
In ADS-B, aircraft equip their systems with GPS receivers and transmitters, sending out regular broadcasts that include position, altitude, speed, and other flight data. These broadcasts are received by ground stations, other aircraft, and satellites, enabling real-time monitoring of the flight.

Real-Time Data Integration
The information gathered by flight tracking systems is continuously processed and shared with air traffic control, airlines, and even passengers. This data helps improve safety, streamline operations, and reduce the risk of accidents.
Data Processing and Monitoring
Flight data collected from tracking systems is transmitted to air traffic control centers. These centers process the information in real-time, updating flight plans and ensuring aircraft are safely separated from one another in the sky.
Airlines also use this data to manage their fleet, monitor flight progress, and make operational decisions such as rerouting flights due to weather or air traffic congestion. In some cases, flight tracking data can also be used to predict potential delays, allowing airlines to adjust schedules accordingly.
Passenger Access to Flight Information
Flight tracking technology has become more accessible to passengers, who can track their flights in real time through mobile apps, airline websites, and other platforms. These systems provide real-time updates on flight status, including arrival times, delays, and gate changes.
Passengers also benefit from increased transparency, as they can view flight paths, altitude, speed, and other details about their flight. This technology helps reduce uncertainty and provides passengers with up-to-date information about their journey.
Flight Tracking for Safety
One of the primary roles of flight tracking systems is ensuring the safety of air travel. By monitoring aircraft positions and flight paths, these systems help air traffic controllers avoid collisions and prevent incidents.
Collision Avoidance and Traffic Management
Flight tracking systems are essential for managing air traffic and ensuring safe separation between aircraft. By constantly updating aircraft positions, air traffic controllers can assess whether planes are on a potential collision course and take action to prevent accidents.
In busy airspace, especially near major airports, flight tracking systems help manage the flow of aircraft, ensuring safe and efficient takeoffs, landings, and transitions between different altitudes.
Emergency Situations
In the event of an emergency, flight tracking systems can help identify issues such as aircraft deviations from their flight path or loss of communication with air traffic controllers. Tracking systems provide real-time data, enabling emergency responders to quickly locate aircraft in distress and intervene as necessary.
For example, if an aircraft experiences a malfunction or enters restricted airspace, flight tracking data allows authorities to take swift action to address the situation and prevent further complications.
Flight Tracking and Fuel Efficiency
In addition to enhancing safety, flight tracking systems play a crucial role in improving fuel efficiency. By providing airlines with accurate and real-time data, these systems help optimize flight routes and reduce fuel consumption.
Optimizing Flight Paths
Flight tracking systems allow airlines to monitor flight progress and adjust flight paths based on factors such as weather conditions, airspace congestion, and fuel consumption. For example, if a flight encounters headwinds, the tracking system can suggest an alternative route to save fuel.
Similarly, by avoiding weather disturbances such as thunderstorms or turbulence, airlines can help reduce delays, improve comfort for passengers, and save fuel. This approach to flight management not only reduces operating costs but also contributes to environmental sustainability by lowering carbon emissions.
Conclusion
Flight tracking systems are essential to the smooth operation of modern aviation. They use radar, satellite, and ADS-B technology to monitor aircraft in real time, providing critical data to air traffic control, airlines, and passengers. These systems improve safety by ensuring aircraft separation, allowing for efficient traffic management, and responding to emergencies. Additionally, flight tracking helps optimize flight paths, improving fuel efficiency and reducing costs. As aviation technology continues to advance, flight tracking systems will play an even more significant role in enhancing the safety, efficiency, and sustainability of air travel.